31 January 2025
How to Choose the Best Mobile App Development Company for Your Business Read More - Premium App & Web Development With Limited-Time Savings  Enjoy 20% Off All App & Web Services
Enjoy 20% Off All App & Web Services  Claim Your Offer Today -
Claim Your Offer Today -
The healthcare app market isn’t just booming, it’s rewriting how care is delivered and how businesses tap into one of the fastest-growing industries.
For startups and enterprises alike, building a healthcare app is no longer just about innovation; it’s about capturing market share and ROI.
With global adoption of healthcare apps rising, the mHealth market is expected to hit billions of dollars in the next few years. Investors and founders are racing to bring scalable, compliant, and user-friendly healthcare solutions to market. But before jumping in, one critical piece of the puzzle demands attention: the cost of app development.
This blog is your detailed guide to understanding healthcare app development cost. We’ll unpack everything from global trends and app categories to compliance, team structures, and budget ranges. If you’re a business leader or startup founder, you’ll walk away with a complete playbook to estimate costs, avoid hidden pitfalls, and make smarter financial decisions on your healthcare app journey.
The healthcare app market is no longer just a trend, it’s a revolution reshaping how patients, doctors, and providers interact. The global digital health market was valued at USD 288.55 billion in 2024 and is expected to rise to USD 946.04 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of 22.2% between 2025 and 2030. This kind of growth signals a massive shift in how healthcare services are delivered and consumed.
Regionally, North America continues to lead thanks to strong adoption of digital health tools, favourable regulations, and high smartphone penetration. Europe is catching up fast, driven by government-backed digital health strategies. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing region, particularly Asia region, where rising internet access and increasing health awareness are fuelling adoption at a record pace.
Within this booming market, a few categories stand out. Telemedicine apps are seeing explosive growth as they make consultations accessible at the click of a button. Electronic Health Record (EHR) apps are improving how providers store, share, and manage patient data securely. And then there’s fitness and wellness apps, which have moved from niche audiences to mainstream popularity as people globally focus on preventive care and healthier lifestyles.
In short, healthcare apps are no longer “nice-to-have.” They are becoming a core channel for care delivery, patient engagement, and health management, creating a fertile ground for businesses and startups looking to enter the space.
So, what’s pushing this demand sky-high? A few powerful forces are at play.
First, cost pressures on healthcare providers are mounting. Hospitals and clinics face the dual challenge of improving patient outcomes while cutting operational cost to build a healthcare app. Healthcare apps help address both, reducing unnecessary hospital visits, optimising staff workload, and streamlining care delivery. For providers, apps are not just about better service; they are about staying financially sustainable in an increasingly competitive healthcare landscape.
Secondly, government initiatives for digital health adoption are playing a huge role. Across the globe, policies are being rolled out to encourage digital transformation in healthcare. For instance, the U.S. government has been pushing interoperability standards for EHR systems, while countries like Asia are actively driving digital health missions. Such initiatives not only improve the ecosystem but also give startups and businesses the confidence that the market is ready and supported.
Together, these drivers make investing in healthcare mobile app development one of the most promising opportunities for businesses and startups today. The demand is there, the ecosystem is supportive, and the technology is more accessible than ever.
Demand tells us why healthcare apps are worth investing in. But to move from inspiration to execution, businesses and startups must understand the true cost of that investment. This brings us to the core of our discussion: healthcare app development cost.
When businesses and startups step into the healthcare app space, one of the first questions they ask is: “How much will it cost?” While this might seem like a straightforward query, the answer is anything but simple. Healthcare apps operate in a regulated, high-stakes industry where precision, compliance, and user trust matter as much as innovation. That means the cost to build a healthcare app isn’t just about coding; it’s about balancing technology, design, security, and compliance, all while meeting the expectations of patients, providers, and regulators.
Before diving into the nitty-gritty of exact numbers, it’s crucial to understand the factors and frameworks that influence healthcare app development cost. Businesses that skip this step often end up underestimating their budgets, facing delays, or struggling with compliance issues later on. A structured approach to cost estimation not only keeps projects on track but also empowers decision-makers to make smart investments.
Let’s break down the foundations of how healthcare app costs are calculated, the pricing models you’ll encounter, and the common misconceptions that can derail budgets.
At its heart, the cost of building a healthcare app can be boiled down to a simple formula:
Effort (hours) × Hourly Rate × Duration.
This looks deceptively simple, but each variable can fluctuate dramatically based on the app’s complexity, the team’s expertise, and the region in which development takes place. Let’s unpack each of these.
Effort refers to the number of development hours required to bring your app to life. A basic symptom-checker app with limited functionality might take 500–700 hours, whereas a full-scale telemedicine platform with video conferencing, EHR integration, AI diagnostics, and HIPAA/GDPR compliance can easily exceed 3,000–5,000 hours.
Factors influencing effort include:
This varies greatly depending on where your development team is located and their level of expertise.
While offshore rates might seem attractive, businesses must weigh the trade-offs. Expertise in healthcare compliance, domain knowledge, and communication efficiency often justifies higher rates in mature markets. Many startups adopt a hybrid model, combining offshore developers for execution and onshore consultants for compliance and strategy.
Duration is how long it takes to complete the project. This depends not only on effort and hourly rate but also on the team size and development methodology.
In short, while the formula seems linear, the interplay between these variables makes the cost to build a healthcare app prediction a nuanced exercise. Businesses should treat this as a framework for conversation with developers rather than a rigid calculator.
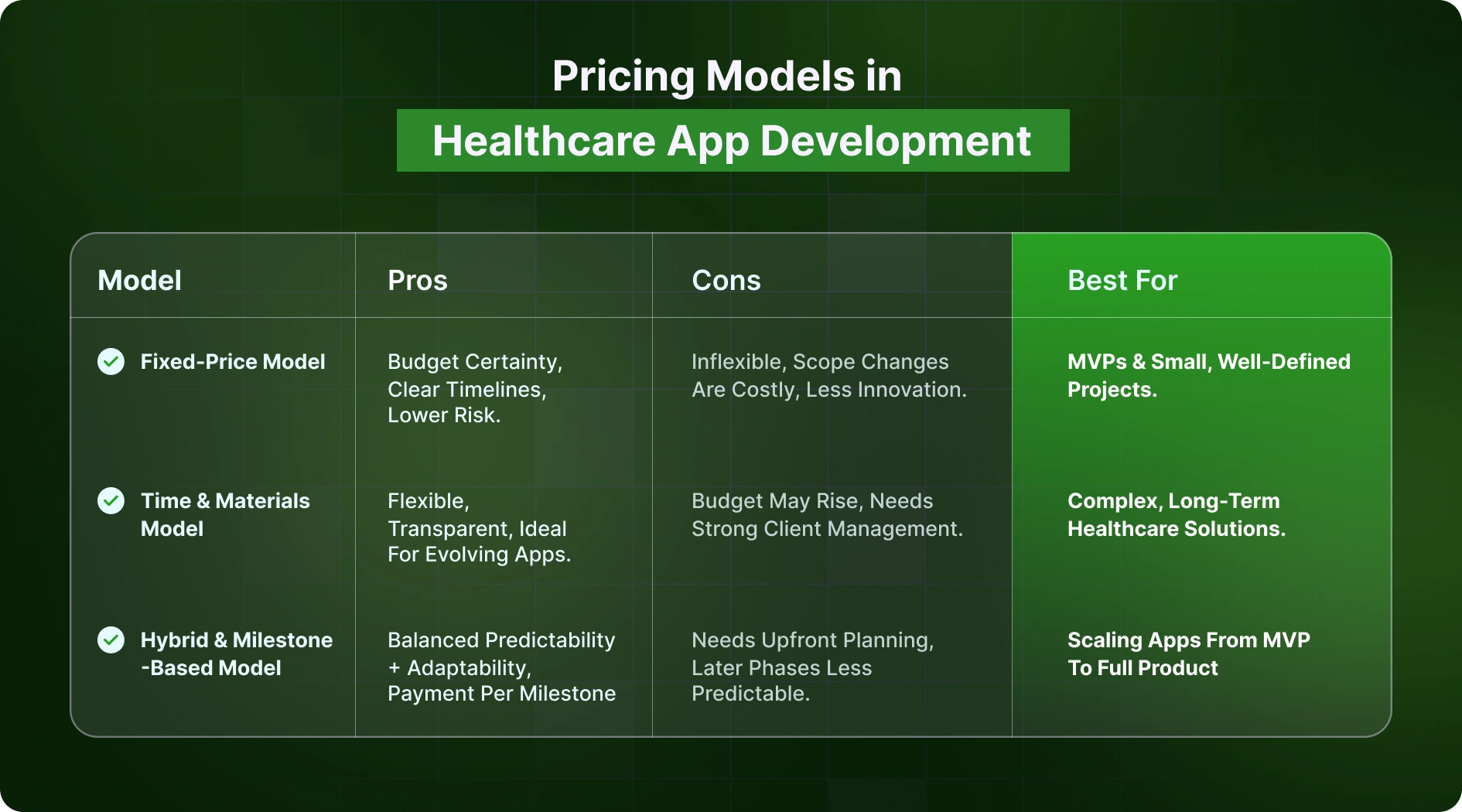
Beyond the formula, how costs are structured plays a huge role in shaping expectations. Different pricing models come with distinct advantages and risks. Choosing the right one depends on your business stage, clarity of requirements, and risk appetite.
In this model, both the scope and cost are agreed upon upfront.
Pros:
Cons:
Best for: MVPs or proof-of-concept apps where the scope is small, requirements are stable, and speed is the priority.
Here, businesses pay for actual hours worked and resources used.
Pros:
Cons:
Best for: Mature startups or enterprises developing long-term healthcare solutions where adaptability is more important than rigid budgeting.
Some businesses prefer a mix, defining clear milestones with fixed costs while keeping flexibility for enhancements in later phases.
Pros:
Cons:
Best for: Businesses scaling from MVP to full product, where clarity exists for initial scope but flexibility is needed later.
Despite clear formulas and models, many businesses enter healthcare app development with misconceptions that can harm their budgets and timelines. Let’s address the most common ones.
Many startups assume they can cut corners with a low-cost build and “fix it later.” In healthcare, this mindset is risky. A poorly built app can fail compliance audits, expose sensitive patient data, or cause reputational damage that no amount of later fixes can fully repair.
Unlike consumer apps, healthcare apps face regulatory scrutiny. If your app doesn’t comply with HIPAA in the U.S. or GDPR in Europe, you risk fines, lawsuits, or outright bans. Rebuilding a non-compliant app often costs more than building it right the first time.
Startups should treat compliance, data security, and user trust as non-negotiable cost to build a healthcare app from day one.
Even when businesses receive seemingly precise estimates, real-world costs often exceed them. Why?
In other words, cost to develop a healthcare app overruns aren’t always a sign of poor planning, they’re often a natural result of working in a dynamic, regulated industry. Businesses can mitigate this by:
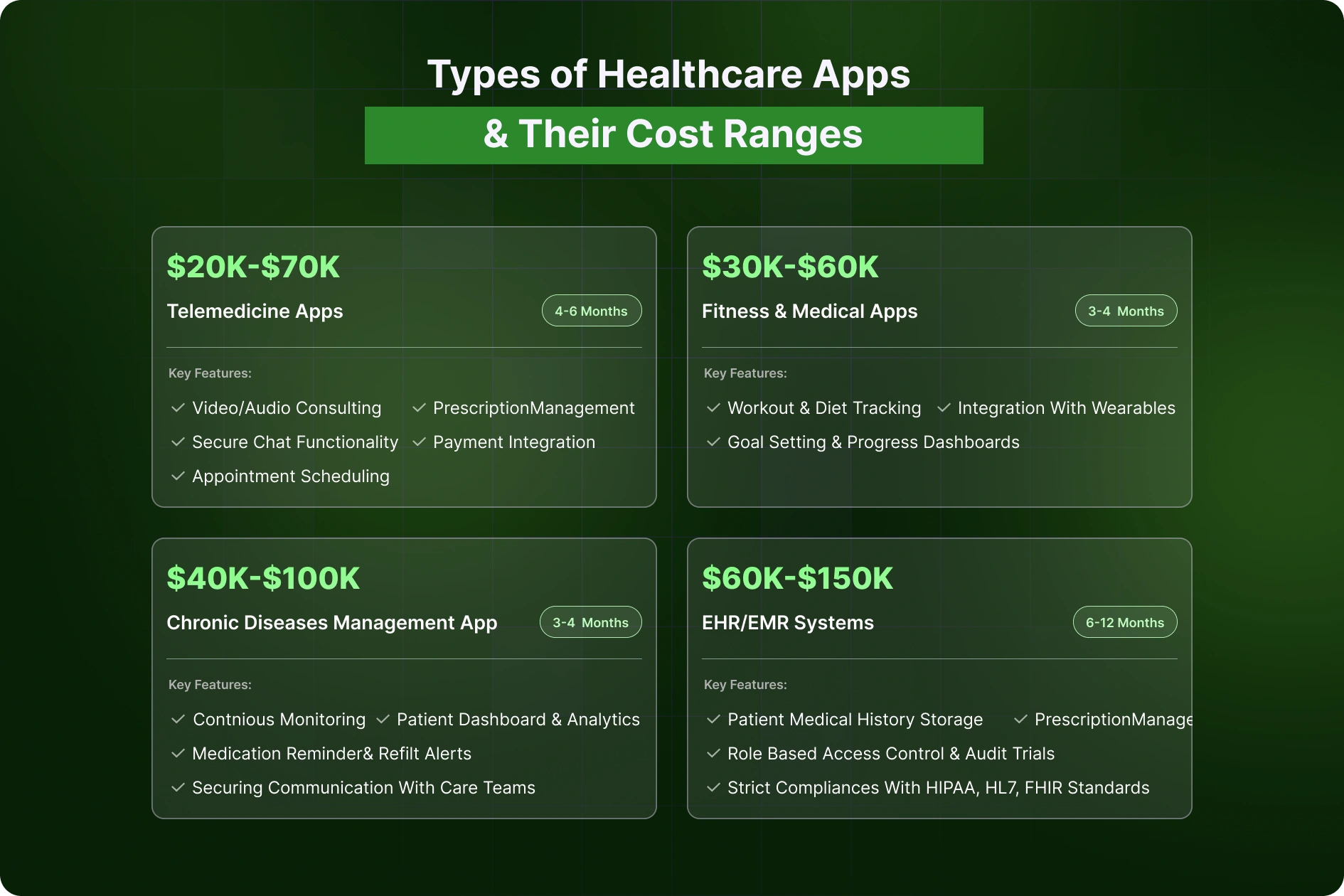
Healthcare is not a one-size-fits-all industry, and the same holds true for healthcare app development. The type of application you want to build plays a decisive role in shaping the overall mhealth app development cost. Each app category comes with unique feature sets, regulatory demands, and integration needs that ultimately influence both timelines and budgets. Below, we break down the most common types of healthcare applications, their typical features, and what you can expect in terms of cost to develop a healthcare app.
Core features: Telemedicine has become the flagship of modern healthcare apps, allowing patients to connect with doctors in real time. At a minimum, telemedicine platforms include:
Advanced builds may integrate AI-based symptom checkers, multilingual support, and interoperability with EHRs.
Cost and timeline: The development cost of developing a healthcare app depends heavily on whether you’re building a basic MVP or a fully compliant, multi-specialty platform. A simple teleconsultation app may start at $20,000–$60,000 and take 4–6 months. Enterprise-grade platforms with HIPAA/GDPR compliance, multi-party video, and hospital integrations can cost between $250,000 and $500,000 with a timeline of 9–12 months.
Core features: Fitness and wellness apps dominate consumer healthcare categories and typically include:
The complexity is relatively lower compared to telemedicine, but syncing with third-party devices and handling real-time data streams requires significant effort.
Cost and timeline: Basic fitness tracking apps can be developed for $40,000–$60,000 within 3–4 months. If you add wearable integration, gamification, and premium subscription modules, the cost to develop a healthcare app can scale to $100,000–$200,000. Long-term, these apps also involve ongoing expenses for API integrations, data storage, and analytics, which startups must factor into the total cost of ownership.
Core features: Chronic disease management apps are designed to support long-term care for patients with conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or asthma. Common features include:
Since these apps directly impact patient outcomes, compliance with healthcare regulations is non-negotiable.
Cost and timeline: Because of their complexity and compliance-heavy build process, costs start at $70,000–$150,000 for a minimal version. A robust solution with device integration, hospital portals, and AI-driven health alerts can easily reach $100,000–$500,000. Development timelines range from 6–12 months.
Core features: Electronic Health Record (EHR) and Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems are mission-critical tools for healthcare providers. Building them is among the most challenging undertakings in this space. Key requirements include:
Cost and timeline: Due to their high security requirements and the need for integration across multiple systems, EHR/EMR apps are among the most expensive healthcare apps to develop. Even a minimal solution may start at $250,000–$400,000. Large-scale systems for hospital networks often exceed $1 million with development timelines stretching from 12 to 24 months. These projects usually require continuous upgrades and regulatory audits, making them an ongoing investment rather than a one-time build.
Core features: Scheduling apps are deceptively complex. While they may seem simple at first glance, the challenge lies in integrating with existing hospital or clinic systems. Core functions include:
Cost and timeline: A basic scheduling app can be built for $30,000–$50,000 in 2–3 months. However, once you add integrations with EHRs, insurance verification, or multi-location hospital systems, costs can jump to $100,000–$200,000.
One often-overlooked factor that impacts cost is whether the app is meant for patients, providers, or both.
Because provider-facing apps require more complex data handling and compliance, they are typically 30–50% costlier than patient-facing counterparts.
Geography plays a critical role in mhealth app development costs, as hourly developer rates vary widely across regions. Here’s a comparison:
Example: A telemedicine MVP costing $100,000 in the US might be delivered for $40,000–$50,000 in Asia, though regulatory expertise may require additional investment in compliance consultants.
Healthcare app development costs vary by type, features, compliance, and region. DevStory helps you manage all these factors, from MVPs to enterprise platforms, with the right mix of expertise, compliance, and cost efficiency.
| Driver | Estimated Cost | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Features | $20,000 – $40,000 | 3–4 months (MVP) |
| Advanced Features | $75,000 – $150,000 | 6–12 months |
| HIPAA (U.S.) | +20–30% development cost | +2–3 months |
| GDPR (Europe) | +$5,000–$15,000 | +1–2 months |
| PIPEDA (Canada) | +$5,000–$10,000 | +1–2 months |
| Compliance Consultants | $5,000–$20,000 (one-time) | Adds extra testing & approval cycles |
When you ask, ‘How much will my healthcare app cost?’ the truth is, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, as costs vary widely depending on your app’s features, the team you hire, and their location. This growing demand is reflected in the global mHealth apps market, which was valued at USD 37.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 86.37 billion by 2030, expanding at a CAGR of 14.8% from 2025 to 2030.
That growth means more competition, so cutting corners on features or compliance just to save money can backfire in the long run.
Instead of looking at healthcare app development cost as a single number, it’s better to break it down into drivers, the factors that really move the needle up or down. The first and biggest? Feature set complexity.
Think of features like the menu in a restaurant. You can go for a simple meal, quick, affordable, and filling. Or you can go for the five-course gourmet experience, premium, complex, and naturally more expensive. Your app features work the same way.
These features don’t take as long to develop, so they keep costs manageable. A basic telemedicine app MVP, for instance, can be built in 3–4 months.
2. Advanced Features ($30,000–100,000)
This is where the costs start climbing, but also where differentiation happens. Advanced features may include:
These not only require more hours of coding but also higher compliance, stronger data security, and sometimes custom APIs. That’s why an advanced healthcare app can take 6–12 months to build.
If there’s one thing you can’t afford to overlook in healthcare app development, it’s compliance. You might have the most user-friendly design and an impressive feature set, but if your app doesn’t meet the necessary regulations, it won’t even make it to market. Worse, non-compliance could cost you millions in fines and a permanent dent in your reputation.
Healthcare is one of the most regulated industries in the world, and for good reason, sensitive patient data is on the line. So, let’s break down the key regulations you’ll likely need to comply with and how they impact both time and cost during development. Compliance consultants often charge project-based fees ranging from $5,000–$20,000, depending on the scope.
If you’re building an app for the U.S. market, HIPAA is non-negotiable. It dictates how patient data (also called Protected Health Information or PHI) should be stored, transmitted, and accessed. That means encrypting data at rest and in transit, secure logins, audit trails, and proper data-sharing protocols.
Here’s the catch: every compliance requirement adds to development hours. For instance, implementing HIPAA-compliant cloud storage or two-factor authentication isn’t a quick plug-and-play, it requires careful planning, testing, and validation. On average, HIPAA compliance can increase development costs by 20–30%, but failing to comply could mean fines as high as $1.5 million per violation.
Planning to launch in Europe? GDPR compliance is a must. While it’s not healthcare-specific, it has strict rules about how personal data is collected, stored, and used. Patients have the right to access, delete, or transfer their data at any time, and your app has to make this possible.
Building GDPR compliance into your app means setting up secure consent forms, allowing easy data export/delete requests, and ensuring that no unnecessary data is stored. All of this adds extra development cycles.
If you’re targeting the Canadian market, PIPEDA rules apply. They’re somewhat similar to GDPR, but with their own twists. Businesses need to obtain meaningful consent, be transparent about how data is used, and report any data breaches promptly.
The challenge here is localisation. Even if your app is already GDPR-compliant, adjusting it to meet PIPEDA’s requirements could mean additional backend tweaks and documentation. It’s not just a legal checkbox; it’s about embedding these practices into the very design of your app.
Now you might wonder, why does compliance eat up so much time and money? The reason is simple: compliance isn’t just code. It involves:
This is why compliance-heavy apps take longer to develop. A simple wellness tracker might go live in 3–4 months, but a HIPAA-compliant telemedicine app could easily stretch to 9–12 months because of all the extra checks.
When businesses think about building a healthcare app, they often picture the final product, sleek interface, seamless integrations, and happy users. But in reality, getting there is a journey made up of several stages, and each stage has its own cost implications. Understanding this lifecycle is essential because expenses don’t just appear at the coding stage. They build up gradually, and if you’re not prepared, it’s easy to underestimate how much you’ll need to invest.
The first step many startups or healthcare organisations take is creating a Proof of Concept (POC). A POC is essentially a small experiment, it helps you validate whether your app idea is technically feasible and worth pursuing. For example, if you’re building an AI-driven diagnostic tool, your POC might test whether the algorithm can interpret a small dataset accurately.
From a cost perspective, POCs are relatively light. They usually involve a small team of developers and data specialists working for a few weeks. Depending on complexity, a POC can cost anywhere between $10,000 and $30,000. The benefit here is obvious: spending a smaller amount upfront can save you from wasting hundreds of thousands later if the idea doesn’t hold up.
Once the POC proves the idea is viable, the next stage is building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). This is the first functional version of your healthcare app that can be tested by real users. Think of it as a skeleton of the final product, it won’t have all the bells and whistles, but it will have just enough features to attract early adopters and gather feedback.
MVPs are where costs start to increase. The timeline usually runs from three to six months, depending on the complexity of features. For example, a simple appointment scheduling app MVP might cost around $40,000–$80,000, while a telemedicine MVP with secure video calls and e-prescriptions can easily cross $100,000–$150,000.
Why does the price jump so much at this stage? Because now you’re not just testing feasibility, you’re ensuring the app works for actual users, complies with security standards, and integrates with basic systems like calendars or payment gateways.
The last stage is scaling the MVP into a full-fledged healthcare app, and this is where businesses often experience ‘sticker shock.’ In countries like the USA, where labour rates and compliance requirements are higher, adding advanced features such as AI diagnostics, wearable integrations, or interoperability with hospital systems can significantly increase healthcare app development cost in USA. A full-scale build can take 9–18 months and cost anywhere from $250,000 to over $1 million, depending on scope.
Here’s where costs compound: you’re not just paying for more features, but also for scalability, advanced compliance checks, performance optimisation, and user experience design. Plus, don’t forget ongoing expenses like maintenance, server costs, and updates to keep up with evolving regulations.
The lifecycle approach — POC → MVP → full-scale — is not just a technical roadmap; it’s also a financial safety net. Each stage allows you to test, refine, and decide whether to move forward. Businesses that skip these steps often overspend or end up building something the market doesn’t actually need. In the USA, where developer rates are higher and strict compliance standards add extra layers of complexity, healthcare app development cost in USA is not a one-off expense; it grows as your app matures. Planning for these stages upfront helps avoid unpleasant surprises and ensures your investment scales in line with real-world demand.
When it comes to healthcare app development, the team you assemble is one of the biggest factors influencing cost. After all, the quality of your app depends not just on the features you want but also on the people building it. Different roles come together to shape the app, from design to code to compliance checks, and each role comes with its own cost range.
Let’s break this down role by role so you get a clear picture.
These are the people who write the actual code. Frontend developers handle the part users interact with, the buttons, forms, dashboards. Backend developers work behind the scenes, making sure your app connects securely with servers, databases, and third-party APIs.
Hourly Rates:
Since healthcare apps often involve complex integrations like EHRs and wearables, backend developers usually take up a larger share of the budget.
A healthcare app must be intuitive. Patients shouldn’t struggle to find a doctor’s slot, and doctors should be able to access dashboards without delays. This is where UI/UX designers step in. They create wireframes, prototypes, and final layouts that are user-friendly and accessible.
A well-designed app not only improves adoption but also saves costs in the long run by reducing redesign needs.
Healthcare apps can’t afford glitches. Imagine a patient missing a medicine reminder because of a bug. QA engineers test your app across devices, operating systems, and user scenarios. They ensure the app meets both functional and compliance requirements.
Testing is often underestimated, but in healthcare, it’s essential. Bugs in this sector are not just inconvenient; they can be dangerous.
With so many moving parts, you need someone to keep the team aligned. Project managers track timelines, budgets, and communication. They act as the bridge between you (the client) and the developers.
While it might feel like an “extra” cost, skipping this role often leads to scope creep, delays, and higher expenses later.
Now comes the big question: should you hire in-house or outsource?
When you’re planning a healthcare app, one of the most important cost factors is the technology stack you choose. In simple terms, the tech stack is the combination of programming languages, frameworks, and tools used to build your app. Think of it like choosing the right building materials before constructing a hospital—what you pick will directly affect quality, durability, speed, and of course, the budget.
Now, let’s break it down.
One of the first big decisions is whether to go native or cross-platform.
So, the decision comes down to your priorities: if you want top-notch performance and scalability, go native. If you’re watching costs and want faster market entry, cross-platform might be the smarter bet.
Beyond the front-end, the backend technology choices also have a huge cost impact. The backend is the engine that keeps your app running, handling data storage, security, authentication, and integration with external systems.
Since healthcare apps deal with sensitive patient data, your tech stack must prioritise encryption, secure databases, and compliance support. For example, using a HIPAA-compliant cloud hosting service costs more than a standard hosting provider, but it’s non-negotiable if you want to avoid fines and legal issues.
A big mistake some startups make is only focusing on initial costs. Choosing a quick, cheaper stack now might lead to higher maintenance costs later. For example, cross-platform solutions might save money at first, but if your app grows into a complex system with multiple integrations, you may end up migrating to native, essentially paying twice.
When it comes to healthcare app development, one of the biggest cost influencers that often gets overlooked is integration. A healthcare app doesn’t exist in isolation. To truly deliver value, it must connect seamlessly with other systems, from hospital databases to wearable devices and secure payment gateways. And while integrations make the app powerful, they also add layers of complexity and cost. Let’s break down the most common integration requirements and what they mean for your budget.
Electronic Health Record (EHR) and Electronic Medical Record (EMR) systems are the backbone of healthcare data. If your app needs to access patient histories, lab results, or treatment records, you’ll need a secure and compliant integration with hospital EHRs.
The challenge? Every hospital might use a different EHR provider, like Epic, Cerner, or Allscripts. These platforms often require custom APIs, strict compliance checks, and sometimes vendor-specific approvals. This alone can add $20,000–$50,000 to your development budget and extend timelines by months. But the payoff is huge, seamless data flow between your app and hospital systems improves patient care and increases adoption among providers.
Whether it’s for teleconsultations, prescription orders, or subscription plans, healthcare apps often need secure payment processing. Integrating payment gateways like Stripe, PayPal, or healthcare-specific processors isn’t just plug-and-play. Developers must ensure compliance with PCI DSS standards and sometimes tailor the payment process for insurance reimbursements or regional rules.
On average, payment integrations cost around $10,000–$25,000, depending on complexity. The good news is, once set up, they offer a steady revenue stream and smoother patient experience, a win-win for both users and providers.
The rise of wearable tech like Fitbit, Apple Watch, and Garmin has changed the way patients monitor their health. Many healthcare apps now need to integrate with wearable APIs to track heart rate, sleep cycles, blood oxygen, or activity levels.
This may sound simple, but ensuring real-time data sync, managing different device protocols, and safeguarding sensitive health metrics add significant complexity. Expect to budget an additional $15,000–$40,000 for robust wearable integrations. And since APIs evolve frequently, there’s also the ongoing cost of maintenance and updates.
Each new integration means:
What does this mean for your project? A healthcare app that needs all three (EHR, payments, wearables) will likely see integration costs climb well past $100,000, making it one of the top budget line items.
This is where Dev Story makes a difference. Our team not only handles the technical side of integrations but also:
By planning for integrations from the start, Dev Story ensures healthcare startups and enterprises launch apps that are secure, compliant, and scalable, without surprises later in development.
When you look at the cost of healthcare app development, it’s not just about writing code. Think of it as a full journey, from idea validation to launch, and then keeping the app alive in a market that never stands still. Each stage of this process has its own price tag, time demands, and level of expertise required. Below, let’s walk through the main phases of development and see how they impact your overall budget.
| Development Stage | Key Activities | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery & Planning | Requirement gathering, compliance planning, and market research | $10,000 – $25,000 |
| UX/UI Design | Wireframes, prototypes, usability testing | $15,000 – $40,000 |
| Backend Architecture | API design, database setup, scalability planning | $20,000 – $60,000 |
| Frontend Development | Native or cross-platform builds, accessibility integration | $25,000 – $80,000 |
| Security Implementation | HIPAA/GDPR compliance, encryption, authentication | $15,000 – $50,000 |
| Testing & QA | Functional, compliance, and load testing | $10,000 – $30,000 |
| Deployment & Launch | App store submission, cloud setup, monitoring tools | $5,000 – $15,000 |
| Post-Launch Maintenance | Bug fixes, updates, scaling, ongoing support | $5,000 – $20,000 per month |
Discovery and Planning
This is the “foundation” stage. Before a single line of code is written, you need to know what you’re building, why, and for whom.
Estimated Cost: $10,000 – $25,000 (depending on complexity and how detailed the planning is).
Timeline: 3–6 weeks.
UX/UI Design
Once the groundwork is done, the next step is designing the user experience (UX) and user interface (UI). In healthcare, design isn’t just about aesthetics, it’s about trust, clarity, and accessibility.
Estimated Cost: $15,000 – $40,000.
Timeline: 4–8 weeks.
Backend Architecture
Behind every smooth healthcare app is a powerful backend. This is where data lives, and for healthcare, that data is often sensitive patient information.
Estimated Cost: $20,000 – $60,000.
Timeline: 6–12 weeks.
Frontend Development
This is the part users interact with, the screens, buttons, and flows. Whether you choose native development (separate apps for iOS and Android) or cross-platform frameworks like Flutter or React Native will heavily influence healthcare app development cost breakdown.
Estimated Cost: $25,000 – $70,000 (native apps cost 30–40% more).
Timeline: 8–16 weeks.
Security Implementation
Security is not optional in healthcare, it’s the backbone. A data breach could mean millions in fines and lost trust.
Estimated Cost: $10,000 – $30,000.
Timeline: 3–5 weeks (often runs parallel with backend work).

Testing & QA
Skipping testing is like skipping a health check-up. It might save a little money now, but the risks are huge.
Estimated Cost: $15,000 – $40,000.
Timeline: 4–8 weeks.
Deployment and Launch
Getting your app live is more than just hitting a button.
Estimated Cost: $5,000 – $15,000.
Timeline: 2–4 weeks.
Post-Launch Maintenance
Once your app is live, the work doesn’t stop. In fact, this is where many businesses underestimate costs.
Estimated Cost: $5,000 – $15,000 per month.
Timeline: Ongoing.
Building a healthcare app is rarely cheap, but high cost doesn’t always mean high value. Many budgets balloon because of unclear priorities, poor planning, or reinventing what already exists. With the right strategies, you can avoid unnecessary spending while still delivering a secure, compliant, and patient-friendly product. Below are proven approaches to optimise and control your healthcare app development cost without compromising on quality.
One of the most effective cost-control measures is developing a Minimum Viable Product (MVP). An MVP focuses on the core functionality needed to prove your concept and meet initial user needs. Instead of building every feature at once, appointment scheduling, EHR integration, payments, wearable sync, and telemedicine, you start small.
For example, if your app is designed for remote consultations, your MVP may only need secure video calling, basic patient profiles, and simple payment integration. Everything else, like wearables or AI-driven diagnostics, can come later.
Benefits of this approach include:
Scaling can be done in phases. Once the MVP gains traction, you reinvest revenue or secure more funding to add advanced features. This phased approach not only spreads healthcare app development costs but ensures you’re building what users actually want.
Developing native apps for iOS and Android separately doubles your telemedicine app development cost. Cross-platform frameworks like Flutter or React Native allow you to build one codebase that works on both platforms.
Benefits:
Limitations:
For most healthcare apps, especially those focused on scheduling, payments, or video calls, cross-platform is more than sufficient. Unless you’re building a feature-intensive solution like real-time diagnostic imaging, frameworks like Flutter can save 30–40% of development costs.
Why build everything from scratch when the healthcare ecosystem already offers pre-built APIs, SDKs, and white-label solutions?
The advantage here is clear, using these pre-built tools cuts months of custom development and ensures compliance is baked in. While these solutions come with licensing costs, they are still cheaper than designing and the cost of developing a healthcare app from scratch.
For startups, especially, white-label platforms can act as a springboard. Instead of spending $500,000 building from the ground up, you can customize a pre-built telehealth app for a fraction of that and still go live quickly.
Talent costs vary dramatically by geography. Hiring developers in the US or UK often costs 2–3 times more than hiring equally skilled professionals in Eastern Europe, Latin America, or South Asia.
Key considerations when outsourcing:
Blended models are also common. For example, you might keep a small in-house team for strategy and compliance while outsourcing coding and design to cost-efficient regions. This hybrid approach balances quality oversight with budget control.
Every bug caught in design or prototyping saves 5–10x the telemedicine app development cost compared to fixing it after launch. That’s why building feedback loops early is crucial.
Practical ways to do this:
By gathering feedback early, you prevent wasted effort on features users don’t want and avoid expensive reworks later. This is especially important in healthcare, where usability directly impacts adoption, if doctors find the app too complex, they won’t use it.
Gone are the days when you needed to invest in expensive on-premise servers. Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer secure, compliant infrastructure that grows with you.
Advantages of cloud-first infrastructure:
This approach not only saves costs but also reduces downtime risk. Instead of spending hundreds of thousands upfront on servers, you might spend just a few thousand annually until your user base expands.

The cost to build a telemedicine mobile app goes beyond coding features; it involves making the right choices at the right time. Many healthcare app development company teams blow their budgets not because of the tech itself, but because of avoidable missteps. Let’s break down the most common pitfalls that send telemedicine app development costs soaring.
One of the biggest budget traps is leaving compliance as an afterthought. HIPAA in the US, GDPR in Europe, and similar regulations worldwide set strict rules around data handling, encryption, and user consent. If you build your app first and try to “bolt on” compliance later, you’re essentially paying for the same work twice.
For example, you might design a patient sign-up flow without proper consent capture. Fixing it later means redesigning the UI, rewriting the backend logic, and redoing the security reviews. Each change costs time, money, and resources that could have been avoided. A compliance-first approach ensures your architecture, data storage, and integrations are built with privacy in mind from day one.
Another silent killer of budgets is fuzzy documentation. When requirements aren’t clearly defined, scope creep sneaks in. Developers build features that stakeholders “thought” they wanted, revisions pile up, and deadlines stretch endlessly.
Imagine asking for a “telemedicine feature” without specifying whether it needs video calls, chat, appointment scheduling, or EHR integration. Each new clarification adds development cycles. Clear requirement documents with user stories, wireframes, and acceptance criteria prevent miscommunication and keep the project on track.
It’s tempting to “figure things out as you go,” but in healthcare, this approach is costly. Every change affects compliance reviews, testing, and integrations, multiplying costs far beyond the initial estimate.
Choosing the wrong tech stack can lock you into years of unnecessary expense. For instance, building natively for iOS and Android separately might give you smooth performance, but it also doubles your telemedicine app development costs if cross-platform frameworks like Flutter or React Native could meet your needs.
On the backend, some teams start with lightweight databases or servers that can’t scale to handle encrypted healthcare records. Later, they’re forced to rebuild on a more robust system, essentially paying for the same functionality twice.
The right choices balance performance, scalability, and cost-efficiency. This doesn’t mean always going with the cheapest option, but it does mean thinking long-term about maintenance and adaptability. A small decision today, like skipping a secure authentication library, can turn into a massive rebuild tomorrow.
Finally, many healthcare startups fall into the trap of building too much, too soon. It’s natural to want your app to have every feature, patient portals, appointment reminders, wearable integrations, and AI chatbots. But loading up your app with untested features before you’ve validated demand is a fast track to budget overruns.
Consider this: you spend six months building a sophisticated wearable integration, only to discover your target users don’t actually use wearables. That’s wasted development time and money.
The smarter path is to launch with a minimum viable product (MVP), something that solves your core problem, gathers feedback, and validates market fit. From there, you can scale features based on real-world demand. Building lean doesn’t just save money upfront, it prevents you from sinking resources into features no one wants.
The cost to build a telemedicine mobile app depends on factors like design, compliance, integrations, and scalability. Costs stack up across technology choices, integrations, compliance checks, and ongoing maintenance. The difference between an app that stays on budget and one that spirals out of control often comes down to foresight. Teams that plan for compliance early, document requirements thoroughly, and choose scalable technologies tend to avoid costly rebuilds later.
At the same time, controlling costs effectively isn’t about cutting corners; it’s about sequencing investments wisely. A phased approach, starting with an MVP, helps validate market demand before committing to advanced features. Using cross-platform frameworks, pre-built solutions, and cloud infrastructure can stretch budgets further without sacrificing quality. Outsourcing to cost-efficient regions and embedding early feedback loops also ensures that resources are spent where they have the most impact. Partnering with an experienced healthcare app development company like Dev Story can help businesses navigate these complexities, providing strategies that manage costs while keeping quality and compliance front and centre.
In healthcare, every decision—whether about data security, integrations, or user experience—carries both financial and regulatory weight. Setting realistic expectations and aligning costs with long-term goals is essential for success. With the right roadmap and the support of a trusted healthcare app development company, building a cost-efficient, high-quality telemedicine app is entirely achievable.