Your competitors have successfully captured another online customer while you’re still dependent on in-person traffic. That one single moment showcases the actual reality of today’s digital-first economy.
After the pandemic the businesses in several industries have marked a massive surge in online shopping, where the Australian ecommerce market is expected to register a CAGR of 13.7% growth from 2025 to 2030 making it one of the fastest-growing markets in the Asia-Pacific region. This new shift means that making an ecommerce website for small business or big enterprises is no longer optional, it’s a transformative and growth strategy.
Are you planning the building of a new ecommerce website Australia? One of the primary questions you may have is likely, “What is the average cost of an eCommerce website?” However, the answer is not as straightforward as a single figure. The e-commerce website development cost lies between $5,000 to $10,000+, depending on the features and complexity.
Small enterprises understand that making a quality online store requires a significant financial investment. They are eager to create one, yet they feel anxious and uncertain due to concerns about the substantial costs involved. They perceive it as a daunting investment and are unsure of their ability to finance it.
In this informative article, we will analyze the true cost to build an ecommerce website in Australia from design and technology to ongoing support and uncover the concealed aspects that are often overlooked. Ranging from ecommerce website for small business to bespoke platforms, you will gain a more comprehensive insight into the costs involved in website development. You’ll also discover ROI expectations, cost-saving strategies, and how to choose the right development partner.
What is an Ecommerce Website?
At its core, an ecommerce website design serves as a digital storefront enabling businesses to market products or services online. In contrast to a static informational site, it offers a comprehensive shopping experience where customers can explore, compare, and buy items without the need to visit a physical store.
The crucial building blocks of an ecommerce website are:

Product Catalog – An organized compilation of products featuring images, descriptions, pricing, and stock status.
Shopping Cart – A digital cart that enables customers to add, examine, and modify their chosen items.
Checkout Process – A structured route for completing purchases, encompassing shipping and delivery information.
Payment Gateway – Secure connections for credit/debit cards, digital wallets, or local options such as Afterpay and PayPal, guaranteeing a seamless transaction.
An ecommerce website simply encompasses more than mere technology. And ecommerce website Australia serves as a tool for growth and sustainability. For startups and entrepreneurs, an ecommerce website offers a budget-friendly method to connect with new customers beyond their region and locality. A boutique retailer or service provider can now market their products across Australia and worldwide rather than being restricted to in-store traffic.
Features like multi-store management, inventory integration, customer relationship management tools, and data-driven marketing strategies help businesses gain advantages in optimizing their operations and maximizing revenue on a large scale.
In today’s competitive environment, building an ecommerce website in Australia has become the demand and necessity of the time. Today’s users demand convenience, quick access, and flawless online shopping experiences and building a secure platform serves as the connection between your brand and your customers, ensuring your relevance in a swiftly expanding digital marketplace, broadening reach, and fostering sustainable growth opportunities for businesses of all sizes.
What is Ecommerce Website Development?
Shopping via online is the first choice of today’s customer. In Australia alone, ecommerce sales continue to grow every year, propelling all size businesses to invest in ecommerce website design Australia giving convenient and contactless shopping.
But the question comes- “ What is ecommerce website development and how has it gained popularity in today’s digital mobile-first world?”
In simple words it is the end-to-end process of creating an online store where products and services are shown, purchased and delivered. Your customer interacts with products or services to shop through this website. An ecommerce website design Australia aims to build a user-friendly and secure platform to sell online that brings high sales and conversions. It combines design, functionality, and security features to create a smooth buying journey.
Core elements include:
- Ecommerce Website Design – Creating layouts that highlight products, simplify navigation, and offer a seamless user experience. A well-crafted ecommerce website design Australia directly impacts how long customers stay and how likely they are to buy.
- Product Management – Setting up catalogs, categories, pricing, and inventory tracking.
- Shopping Cart & Checkout – Streamlined processes that reduce friction and cart abandonment.
- Payment Integrations – Secure options such as PayPal, Stripe, and Afterpay in AUD.
- Security Features – SSL certificates, fraud detection, and data encryption.
- SEO & Mobile Optimization – Ensuring the site ranks on Google and works flawlessly across devices.
- Customer Support Tools – Features like chatbots, return policies, and order tracking to enhance trust.
Extend your reach beyond the local customer with your own ecommerce website Australia.
On the other hand, ecommerce websites for big companies or enterprises can reach a global audience by integrating advanced AI-powered features like CRM integrations, multi-store setups, and automation tools enable large-scale operations.
When evaluating the budget of an ecommerce website cost Australia, businesses must account not only for design and development but also for compliance with GST, consumer law standards, and integrations with local logistics. Skipping these details can affect long-term ROI, making development even more critical.
Think of having your own ecommerce website Australia then get in touch with Dev Story and build a secure, growth-driven platform that aligns with your business goals and the expectations of modern Australian shoppers.
Analysis of Ecommerce Market in Australia
“Your customers are already taping—are you ready to hold them back?”
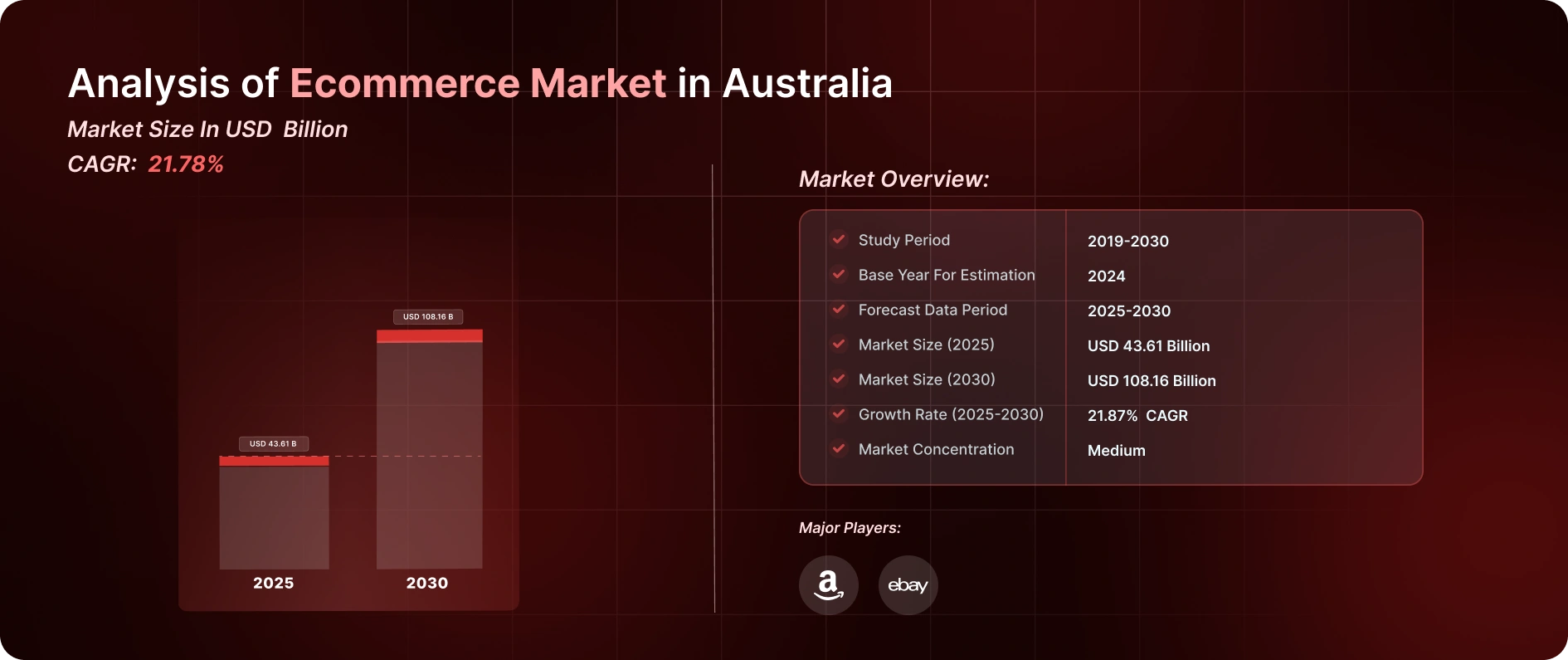
In terms of Business Model, the B2C segment represented 62% of the e-commerce market share in Australia for the year 2024, while the B2B segment is anticipated to achieve the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.8% through 2030.
Regarding Device usage, smartphones led the market with a revenue share of 65% in 2024; additionally, the category of “other devices”—which includes voice assistants, smart TVs, and IoT devices—is expected to expand at a CAGR of 12.3% until 2030.
Concerning Payment Method, credit and debit cards maintained a 45% share of the e-commerce market size in Australia in 2024, whereas Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services are projected to experience the most significant growth with a CAGR of 14.7% through 2030.
Source- Mordor Intelligence
Australia’s ecommerce sector is experiencing significant growth. In 2024, Australians are projected to have spent approximately AU$69 billion online, reflecting a 12% increase compared to the previous year. Online sales now represent 16.8% of total retail, a notable rise from about 10% prior to the pandemic, according to Fox & Lee.
Industry predictions suggest that online shopping will constitute 18% of total retail by 2025, with the possibility of reaching 22% by 2026, as ecommerce revenues are expected to range between A$67 and A$87 billion, according to Siecap.
Mobile devices are a key driver of this expansion. Approximately 73% of Australian consumers utilize their smartphones for shopping, with 44% favoring mobile web browsing and 33% opting for shopping applications to complete their purchases, as reported by au.yougov.com.
Why is this significant for your business?
Regardless of whether you are running a small ecommerce site in Australia or overseeing a platform for extensive operations, investing in an ecommerce website design Australia for businesses has become imperative. It is no longer a matter of choice. Given the rapid changes in market trends and customer behavior, maintaining a robust online presence is crucial for capturing market share, remaining relevant, and surpassing competitors.
Industry leaders like Amazon, Alibaba, Shopify, eBay, and Walmart, have given commerce an upswing in online selling. Give your customers a plethora of product choices, complimentary shipping, competitive pricing, and enticing discounts.
As the e-commerce industry is experiencing a remarkable surge, let us know the different types of Ecommerce websites and understand their core differences will help you select the most suitable website type for your enterprise, allowing you to capitalize on the burgeoning e-commerce sector.
Different Types of Ecommerce Websites
If you are searching for the most profitable eCommerce business, then explore the options below and start building your online shop. Each eCommerce model serves a unique audience, revenue structure, and growth strategy. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right approach, optimize costs, scale efficiently, and build a sustainable online business aligned with your goals.

1. Individual Brand
A dedicated brand or vendor-specific e-commerce website enables retailers to oversee their storefronts. This is a prevalent format for online commerce.
The store owner acts as the sole seller. You have the ability to focus on your target customers and sell directly to them without intermediaries. No one is permitted to sell products without the owner’s consent.
The website showcases products and services from a single business or vendor. You can introduce products, establish pricing, and interact with customers directly. There are no third parties involved, as businesses market their own products.
2. Multi-Vendor Retailers
A multi-vendor or online retail platform consists of numerous sellers managed by a single website owner.
Sellers have the opportunity to operate their own independent storefronts to market their products. Nevertheless, the website owner is a separate entity. The website owner is responsible for the overhead ecommerce website cost associated with hosting and backend development. In return, sellers pay a small percentage of their revenue to the site owner.
This arrangement enables sellers to gauge customer demand prior to launching their own websites. However, it also means that sellers have limited control over the website’s rules and regulations. Compliance with the website’s policies is mandatory, and any breach of these policies could result in the suspension of the seller’s store.
Additionally, achieving a higher ranking in website search results may prove challenging due to competition with other sellers. Customers might struggle to locate your store among the multitude of vendors.
On the positive side, sellers benefit from operational services provided by the website owner. These services include order processing and shipping. The website owner also manages payment methods and offers inventory management services.
A successful multi-vendor website can lead to increased product sales. Buyers appreciate the convenience of purchasing a variety of items from a single platform, including household goods, electronics, and fashion products.
3. Marketplaces
Marketplace websites serve as a platform that connects vendors and buyers. The owner of the marketplace is responsible for processing customer transactions. Vendors and wholesalers handle the shipment and fulfillment of products.
Numerous individual sellers list their products for sale. Online marketplaces enforce rules and restrictions regarding the items that can be sold. You have the opportunity to add your products to the marketplace to earn a profit. Employ marketing strategies and promotions to attract more customers and enhance conversion rates.
Marketplace websites are favored by both vendors and buyers. They provide a diverse array of products from various sellers.
Within these marketplaces, the owner manages customer transactions. Shipment and fulfillment responsibilities are managed by the vendors and wholesalers who create e-commerce websites.
Nevertheless, it is crucial to remember that online marketplaces have regulations concerning what can be sold. Furthermore, establishing a distinct identity on the platform can be challenging.
4. Affiliate Websites
An affiliate website is a platform where you promote and sell products from other brands in return for a commission.
Your website should already have a steady flow of traffic. You can leverage affiliate marketing and sales to create revenue. The owner of the website collaborates with brands to incorporate affiliate links.
Additionally, you can earn commissions based on user actions taken on the latest ecommerce companies.
The terms are established with the merchants according to their specifications.
Affiliate payouts consist of the following:
- Direct Sales – Receive a commission from the sale of a product or service.
- Leads – Earn commissions for actions such as social media follows, content downloads, etc.
- Clicks – Generate affiliate revenue on a cost-per-click basis from website visitors.
For a successful affiliate marketing business, driving consistent traffic through promotion is only half the battle. You need a high-converting website to capture that interest. Collaborating with a web development companies ensures your site is engineered for performance, security, and search engine visibility, creating a seamless user experience that directly translates into higher commission earnings.
An affiliate website serves as a superb choice for individuals seeking to market products from other brands in return for a commission. To increase commissions, the website must have a consistent flow of traffic. It is essential to focus on marketing and promotional efforts to generate income.
Six E-Commerce Business Models

1. Business-To-Business (B2B)
As indicated by its name, B2B stores facilitate transactions between two businesses — either manufacturers and wholesalers or wholesalers and retailers — via an online platform.
This model generally encompasses substantial product quantities or extended service contracts between the involved parties. It’s one of the fastest-growing eCommerce sales models, with estimates exceeding $10 billion in volume in the U.S.
- B2B enables businesses to engage with pertinent distributors and suppliers through a digital platform, which can yield numerous advantages:
- Automated sales processes on both sides
- Reduced infrastructure and overhead expenses
- Enhanced growth prospects
- Elimination of intermediaries
- Improved productivity and partner relationships
2. Business-To-Consumer (B2C)
Arguably the most recognized model, B2C pertains to transactions between businesses and consumers.
It encompasses all e-Stores that sell products directly to their intended audience and offers the following advantages:
- Lower prices due to the absence of third-party involvement
- Broader global reach in comparison to physical stores
- Sophisticated marketing strategies informed by user data
3. Consumer-To-Consumer (C2C)
The subsequent business model revolves around consumer-to-consumer transactions, where businesses do not play a direct role. It presents a rather informal situation — consider platforms like Facebook Marketplace, Amazon, or eBay listings.
This easily accessible and convenient method for buying and selling goods offers several advantages:
- Transforming unused items into consumer profit
- Expanding the customer reach
- Leveraging an “umbrella” platform to enhance individual credibility
4. Consumer-To-Business (C2B)
As independent entrepreneurs, consumers have the ability to provide goods or services to businesses.
Notable examples are freelance platforms like Upwork and Fiverr, where individuals can present their expertise to companies seeking assistance.
This trend aligns with the growth of the gig economy, indicating that individuals are increasingly pursuing flexible employment opportunities while organizations are more inclined to delegate tasks to freelancers rather than recruiting new employees.
5. Direct-to-Consumer (DTC or D2C)
DTC websites enable brands to market their products directly to consumers, eliminating the need for third-party retailers. This approach provides businesses with complete authority over branding, pricing, and customer interactions.
Examples of DTC websites include Warby Parker, Glossier, and Allbirds—brands that function exclusively online and engage directly with their target audience. DTC facilitates greater personalization and increased profit margins. It is an expanding trend, particularly among startups and niche brands.
6. Subscription-Based E-commerce
This model offers products or services on a recurring schedule, typically monthly or quarterly. Companies such as Dollar Shave Club and Netflix are prominent leaders in subscription eCommerce. The objective is to foster customer loyalty through convenience and value.
Subscription eCommerce necessitates reliable service, automated billing, and adaptable cancellation options. It is particularly suitable for consumables, digital services, or content platforms.
7. White-label
It entails a company developing a service and permitting other companies to rebrand and market it as their own.
A prime example of a white-label ecommerce platform is Shopify. It enables businesses to establish their own online stores utilizing the Shopify infrastructure. This approach is commonly adopted in the print-on-demand sector, where entrepreneurs can offer personalized products such as print on demand phone cases without managing production or stock.
Every ecommerce business model possesses distinct characteristics and obstacles. The selection of the appropriate business model is contingent upon a company’s objectives, target demographic, and the products or services it provides.

Australian Market Specific Considerations
Creating an ecommerce website for businesses in Australia involves more than merely implementing global best practices. Local payment preferences, shipping infrastructure, compliance regulations, and cultural awareness all play a significant role in the development of an ecommerce platform. These elements also affect the overall cost of building an ecommerce website in Australia, making it crucial for companies to plan their budgets wisely. Below are the key considerations.
1. Payment Gateways
Australian consumers anticipate flexible and secure payment methods. Notable gateways include Afterpay, Zip, PayPal, Stripe, and direct local bank integrations. Providing Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) options has become nearly essential for brands in fashion, lifestyle, and consumer electronics.
- Cost impact: Standard gateway integrations can range from A$2,000 to A$5,000, while BNPL services may incur additional ecommerce website cost of A$3,000 to A$7,000 depending on the provider’s APIs.
2. Shipping Integrations
An efficient checkout process is also reliant on effective shipping solutions. Australian ecommerce platforms typically connect with Australia Post, StarTrack, and major courier networks to offer real-time shipping rates, tracking, and delivery alternatives.
- Cost impact: Basic shipping setups begin at A$1,500, whereas advanced multi-carrier systems with automation and warehouse integrations can surpass A$10,000.
3. Tax Compliance (GST)
In contrast to some other markets, Australia mandates the automation of Goods and Services Tax (GST), with a clear differentiation between business and consumer pricing. This is vital for both B2B and B2C ecommerce.
- Cost impact: A straightforward GST setup may cost approximately A$1,000 to A$3,000, while more intricate systems (such as multi-region pricing and wholesale versus retail accounts) can exceed A$5,000.
4. Consumer Law Compliance
The ACCC (Australian Competition and Consumer Commission) imposes stringent regulations regarding refund policies, warranties, and product representations. Websites are required to explicitly outline return terms and safeguard customer rights. Failure to comply may result in penalties and harm to reputation.
- Cost impact: The cost to create an ecommerce website in Australia for legal advice and compliance features typically range from A$1,500 to A$5,000 during the development phase.
5. Local Hosting & Data Sovereignty
Performance is crucial for conversions, particularly given Australia’s vast geographic expanse. Hosting your website on servers situated in Australia, complemented by a Content Delivery Network (CDN), guarantees quicker load times and adherence to data sovereignty regulations.
- Cost impact: Hosting expenses can vary from A$500 to A$2,000 annually for small enterprises, while enterprise-level hosting with CDN support may surpass A$10,000 per year.
Cultural sensitivity in the design of ecommerce websites is becoming increasingly vital, especially for businesses that operate within or cater to diverse communities. Thoughtful design choices, inclusive imagery, and recognition of Traditional Custodians can foster trust and enhance brand reputation.
- Cost impact: Although the direct cost to develop an ecommerce website in Australia may be relatively low (A$500 to A$2,000 for inclusive design modifications), the long-term value of the brand and alignment with the community are substantial.
Why These Considerations Are Important
Taking into account these local regulations is not merely a matter of compliance—it is essential for crafting an ecommerce experience that appeals to Australian consumers. Neglecting these factors may lead to increased operational risks and customer dissatisfaction, which could ultimately elevate the expenses associated with establishing an ecommerce website in Australia over time.
When inquiring, “What constitutes the cost to develop an ecommerce website in Australia?” The response is straightforward: it involves more than just constructing a digital storefront; it requires customization to suit the market you are targeting. In the context of Australia, this entails addressing aspects such as payments, shipping, compliance, hosting, and cultural awareness.
Depending on the degree of customization required, the additional expenses for developing an ecommerce website in Australia to fulfill these criteria can vary from A$7,000 to A$30,000, in addition to the standard development costs.

How Much Does It Cost to Create An Ecommerce website in Australia?
One of the most frequently posed inquiries by businesses contemplating a transition to digital is: “What is the typical expense associated with an ecommerce website?” The response is contingent upon the project’s scope, design specifications, and technical intricacies. In Australia, the cost of an ecommerce website generally falls within the range of A$10,000 to A$50,000+—however, let us delve deeper into the specifics.
Answer: “How much does it cost to build an eCommerce website in Australia?“
Cost variations based on type.
Tier 1: Basic Starter Store (A$5,000 – A$15,000)
Ideal for startups and small businesses launching online, this tier delivers a functional eCommerce presence with essential features, fast setup, and minimal customization to validate products quickly.
Best for: Small enterprises, emerging brands, fewer than 50 products.
Includes: Pre-designed theme, fundamental payment/shipping configuration, essential pages.
Tier 2: Customized Mid-Market Store (A$15,000 – A$45,000)
Designed for growing brands, this tier offers tailored design, advanced integrations, and scalable functionality that supports expanding catalogs, subscriptions, and operational efficiency.
Suitable for: Expanding businesses with a distinct brand identity, requiring tailored functionality.
Includes: Custom design, integration with ERPs/CRMs, advanced product filtering, subscription models.
Tier 3: Large-Scale Enterprise Solution (A$45,000 – A$100,000+)
Built for enterprise-level operations, this tier provides a fully customized, secure, and scalable eCommerce ecosystem capable of handling complex workflows, high traffic, and multi-store management.
Suitable for: High-volume enterprises, intricate catalogs, customized workflows.
Includes: Completely bespoke architecture, multi-store management, enhanced security, continuous dedicated support.
- The Hidden Costs: Beyond Development
- Domain & Hosting: A$200 – A$2,000+/year
- SSL Certificate: A$100 – A$500/year
- Maintenance & Support: A$1,500 – A$10,000+/year
- Marketing & SEO: Ongoing budget necessary.
E-commerce Website Development Cost
The cost to develop an ecommerce website in Australia starts at around A$10,000 for basic builds and can exceed A$50,000 for advanced platforms. This includes backend development, product catalog setup, integrations with payment gateways and shipping providers, database management, and security compliance.
- Basic online store (A$10,000–A$20,000): Suitable for ecommerce website for small business with limited products, essential checkout, and simple design.
- Mid-sized ecommerce platform (A$20,000–A$35,000): Custom functionality, integrations with CRMs/ERPs, and advanced product filtering.
- Enterprise-level solution (A$35,000–A$50,000+): Bespoke architecture, multi-store management, high traffic scalability, and dedicated support.
Ecommerce Website Design Cost
Design is equally important because it directly impacts conversions. The ecommerce website design cost in Australia usually falls between A$8,000 and A$25,000+, depending on customization and branding needs.
- Template-based design (A$8,000–A$12,000): Affordable option with pre-designed layouts, best for startups and small businesses.
- Custom design (A$12,000–A$20,000): Tailored layouts, brand-specific visuals, and better user experience.
- Advanced design (A$20,000–A$25,000+): High-end visuals, animations, UX research, and personalization features.
Hidden and Ongoing Costs
Beyond the upfront website development expense, running a successful eCommerce business in Australia involves several hidden and ongoing costs. These recurring investments are essential for maintaining performance, security, visibility, and scalability. Planning for these expenses early helps businesses avoid unexpected budget overruns and ensures long-term operational stability and sustainable growth.
Beyond initial development, businesses should plan for:
- Domain & Hosting: A$200–A$2,000 annually.
- SSL Certificates & Security: A$100–A$500 annually.
- Maintenance & Support: A$1,500–A$10,000+ per year.
Marketing & SEO: Ongoing investment depending on growth goals.
Factors Influencing Ecommerce Website Cost in Australia
 The expense associated with creating an ecommerce website Australia can fluctuate considerably based on various factors. While certain businesses might allocate approximately A$8,000–A$15,000 for a basic online store, others could invest A$50,000 or more for a solution of enterprise caliber. To assist businesses in realistic planning, here are the ten primary factors that affect the cost of ecommerce website development in Australia.
The expense associated with creating an ecommerce website Australia can fluctuate considerably based on various factors. While certain businesses might allocate approximately A$8,000–A$15,000 for a basic online store, others could invest A$50,000 or more for a solution of enterprise caliber. To assist businesses in realistic planning, here are the ten primary factors that affect the cost of ecommerce website development in Australia.
1. Website Design & User Experience (A$3,000 – A$20,000+)
The design is frequently the most prominent feature of any ecommerce website. A straightforward, template-based design incurs significantly lower costs compared to a fully customized design that is specifically tailored to your brand.
- Template design: A$3,000 – A$7,000
- Custom UI/UX design: A$10,000 – A$20,000+
For businesses, investing in professional ecommerce website design in Australia guarantees enhanced usability, increased conversions, and greater brand credibility.
2. Development Platform or Technology Stack (A$2,000 – A$50,000+)
The platform you select has a direct effect on both initial expenses and long-term scalability.
- Shopify: A$2,000 – A$10,000 for setup & customization.
- WooCommerce: A$5,000 – A$15,000 (depending on plugins & hosting).
- Magento / Adobe Commerce: A$15,000 – A$50,000+ (enterprise-ready).
- Custom-built solutions: A$25,000 – A$100,000+.
If your business expects rapid growth or complex operations, investing more initially in a scalable platform may lead to cost savings in the future.
3. Features & Functionalities (A$5,000 – A$25,000+)
The intricacy of your ecommerce features significantly impacts the cost to develop an ecommerce website in Australia.
- Basic features include: product catalog, shopping cart, checkout, and payment gateway (A$5,000 – A$10,000).
- Advanced features encompass: AI-driven recommendations, multi-language support, subscription models, and loyalty programs (A$15,000 – A$25,000+).
Each additional functionality necessitates development hours, thereby increasing both the cost and the timeline.
4. Business Scale & Catalog Size (A$3,000 – A$50,000+)
The extent of your product catalog and the scale of your business operations affect the total cost.
- For small business websites (<100 products): A$3,000 – A$8,000.
- For medium-sized businesses (500–1,000 products): A$10,000 – A$20,000.
- For enterprises with thousands of SKUs: A$20,000 – A$50,000+.
An ecommerce website tailored for a small business will inherently be less expensive, but scaling up necessitates a more robust architecture, automation, and inventory integrations.
5. Payment Gateway & Checkout Systems (A$1,000 – A$10,000)
Customers in Australia anticipate secure and versatile payment options. The costs fluctuate based on the number and complexity of integrations:
- Basic gateways include: PayPal, Stripe (A$1,000 – A$3,000).
- Local alternatives include: Afterpay, Zip, POLi (A$3,000 – A$7,000).
- Advanced multi-currency and BNPL setups range from A$7,000 – A$10,000.
The greater the payment flexibility you provide, the higher the associated development costs.
6. Security & Compliance (A$1,000 – A$5,000+)
In the realm of online transactions, security is imperative. The associated costs encompass:
- SSL certificates: A$100 – A$500 per year.
- PCI DSS compliance: A$1,000 – A$5,000.
- Fraud prevention tools: Additional recurring expenses.
Adhering to compliance standards in Australia not only fosters trust but also mitigates legal risks.
7. Third-Party Integrations (A$2,000 – A$15,000+)
Numerous businesses connect their ecommerce platforms with CRMs, ERPs, shipping solutions, or marketing automation systems.
- Basic shipping integration (Australia Post, StarTrack): A$2,000 – A$5,000.
- ERP/CRM integrations (MYOB, Xero, Salesforce): A$5,000 – A$15,000+.
The necessity for more integrations correlates with increased costs.
8. Hosting & Infrastructure (A$500 – A$5,000+ annually)
The hosting environment of your website significantly influences its speed, reliability, and compliance.
- Shared hosting: A$500 – A$1,000 per year.
- Cloud hosting (AWS, Azure, GCP): A$2,000 – A$5,000+/year.
- Dedicated enterprise hosting: A$10,000+/year.
For an ecommerce site in Australia, utilizing local hosting can enhance performance and ensure data sovereignty.
9. Maintenance & Ongoing Support (A$1,500 – A$10,000+/year)
Ecommerce entails ongoing expenses. Businesses should allocate budget for:
- Regular updates.
- Bug fixes.
- Security patches.
- New feature enhancements.
Consistent maintenance guarantees seamless operations and safeguards your investment over the long term.
10. Marketing & SEO Preparedness (A$2,000 – A$15,000+)
A properly structured ecommerce website must also be optimized for search engines.
- Basic SEO configuration: A$2,000 – A$5,000.
- Advanced SEO along with content strategy: A$10,000 – A$15,000+.
- Ongoing PPC/advertising & digital marketing: Additional monthly expenditure.
In the absence of this, even the most well-constructed ecommerce website will fail to generate traffic or conversions.
Final Thoughts on Ecommerce Website Cost Considerations
When companies inquire, “What is the typical cost of an ecommerce website in Australia?” The response is that it varies based on these 10 factors. A fundamental ecommerce website for small business may range from A$5,000 – A$15,000, whereas a large-scale ecommerce platform for enterprises can easily surpass A$50,000.
Careful planning around these ecommerce website cost Australia determinants aids in preventing budgetary surprises and guarantees optimal ROI from your ecommerce investment.

Budgeting and Timeline Planning
Creating an ecommerce website Australia involves more than just incorporating features; it necessitates astute financial planning and realistic timelines. Successful online businesses meticulously allocate their budgets, establish milestones, and recognize that high-quality ecommerce platforms require a phased development approach. Whether developing an ecommerce website for small business or a large-scale enterprise solution, having a well-structured roadmap is essential to keep the project on course and achieve measurable ROI.
The typical progression of an ecommerce website project is as follows:
Phase 1: Discovery and Planning (4–6 weeks, ~20% of budget)
This phase entails gathering requirements, conducting competitor analysis, and mapping out customer journeys. The development team delineates the project scope, selects the appropriate platform, and estimates the costs associated with the ecommerce website. Effective planning mitigates the risk of scope creep and ensures that the final website aligns with the business objectives.
Phase 2: Design and Approval (6–8 weeks, ~30% of budget)
At this stage, the focus transitions to the design of the ecommerce website in Australia, which includes creating wireframes, prototypes, and branding elements. Decisions regarding user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) are finalized. For small businesses, this phase guarantees a professional appearance, while larger enterprises often necessitate custom layouts and optimization for multiple devices. Approval checkpoints enable stakeholders to verify alignment before the development phase commences.
Phase 3: Development and Testing (8–12 weeks, ~40% of budget)
This phase is where the actual site construction occurs, integrating product catalogs, shopping carts, payment gateways, and various integrations. Testing is crucial: aspects such as speed, security, and mobile responsiveness must adhere to established standards. For a scalable ecommerce website in Australia, compliance with GST, local logistics, and ACCC consumer laws is also confirmed during this phase.
Phase 4: Launch and Optimization (2–4 weeks, ~10% of budget)
After testing is finalized, the site is launched. Following the launch, the team observes user behavior, addresses any bugs, and optimizes performance. Businesses frequently allocate resources for SEO and analytics integration.
Ecommerce Website Cost Australia Saving Tips for Businesses
The expense associated with creating an ecommerce website Australia can fluctuate significantly based on various factors such as scope, design, and technology. Although it may be appealing to incorporate every advanced feature from the outset, businesses—particularly startups—should focus on making prudent investments. Below are four effective strategies to minimize costs without sacrificing quality.
1. Begin with an MVP (Minimum Viable Product)
Rather than developing a fully equipped platform, initiate your project with an MVP that encompasses only the fundamental features—product catalog, shopping cart, payment gateway, and security. This strategy not only reduces the cost of establishing an ecommerce website in Australia but also enables you to validate your business concept prior to expansion. Once the site begins to attract users, additional features such as loyalty programs, AI chatbots, or enhanced personalization can be incorporated in a strategic manner.
2. Opt for Scalable Platforms
Selecting the appropriate technology stack can greatly influence long-term expenses. Platforms such as Shopify, WooCommerce, or Magento provide scalable solutions that allow for growth as your business expands. For a small startup, this approach helps avoid substantial upfront custom development costs, while larger enterprises benefit from the flexibility to adapt as customer demand rises. Choosing scalability ensures that the average cost of an ecommerce website remains manageable over time.
3. Refrain from Unnecessary Custom Features at Launch
Custom features such as advanced search algorithms, intricate integrations, or gamification elements may seem attractive but can rapidly escalate development budgets. For an ecommerce website aimed at small businesses, it is more practical to focus on core functionalities initially. Businesses can gradually introduce custom features once they achieve consistent sales and gain a better understanding of customer requirements.
4. Collaborate with the Right Development Partner
Choosing the appropriate agency or technology partner is essential. Skilled developers can streamline the process, provide precise estimates of the cost to build an ecommerce website in Australia, and assist in avoiding expensive errors. A trustworthy partner also ensures that the project stays on track and within budget.
5. Leverage Ready-Made Themes and Plugins
Utilizing pre-built themes and trusted plugins can significantly lower design and development costs. Most modern ecommerce platforms offer professionally designed templates and feature-rich extensions for payments, shipping, SEO, and analytics. Instead of building everything from scratch, businesses can customize these solutions to suit their brand, reducing both development time and the overall ecommerce website cost in Australia.
6. Plan Integrations Strategically
Third-party integrations such as CRM systems, accounting software, marketing tools, or inventory management platforms can add to development expenses if not planned carefully. Prioritizing essential integrations at launch and postponing advanced tools helps control initial costs. A phased integration strategy allows businesses to scale operations efficiently while keeping ecommerce website development expenses predictable.
7. Invest in Performance and SEO Early
Optimizing website performance and SEO during development reduces long-term marketing and maintenance costs. A fast-loading, search-engine-friendly ecommerce site attracts organic traffic, lowers paid advertising dependency, and improves conversion rates. Addressing performance optimization early prevents costly rework later and maximizes returns on your ecommerce investment in Australia.

Wrapping Up
Understanding the investment required for an ecommerce website in Australia goes beyond the initial price. It’s about funding a powerful platform designed for growth, building customer loyalty, and delivering lasting value.
As you research, you’ll find a range of figures. A small business ecommerce website often requires an initial investment of $10,000 to $25,000. For larger enterprises with complex needs, this can easily rise to $50,000 or more. So, when asking for an average cost, the true answer always depends on your business’s scale, required features, and level of customization.
However, the cost should never be the only consideration. A more important question is: What strategic advantages will a professional ecommerce build bring? A superior site does more than just process transactions; it delivers a seamless user experience, streamlines your operations, ensures compliance with Australian consumer law and GST, and positions your brand for success in a digital-first economy.
Every business is unique, demanding a tailored strategy. This is where partnering with the right web development company in Australia makes all the difference. They can ensure your platform is built on a solid foundation, whether you’re a small business needing a cost-effective launch or a larger brand requiring sophisticated integrations and scalability.
When you consider the cost to build an ecommerce website, remember it’s an investment in value, not just an expense. A strategically developed site protects your business’s future and unlocks new growth channels. This is the core principle at Devstory, where we believe in building digital commerce solutions that are engineered for success.
Are you ready to develop a secure, scalable, and high-converting ecommerce website? Contact our specialists today, and let’s create a custom solution that turns your vision into a reality, aligned perfectly with your goals and budget.












